The Ultimate Demise Of The Euro Union

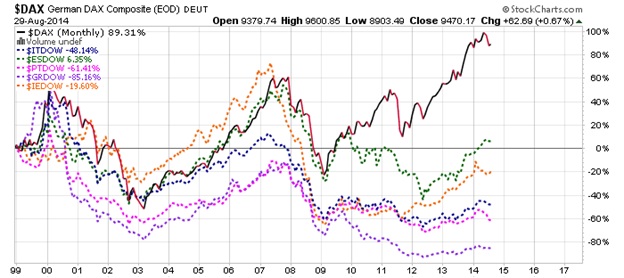

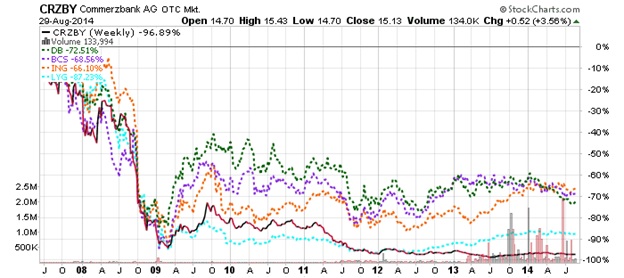

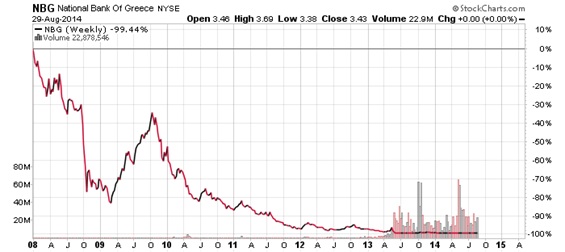
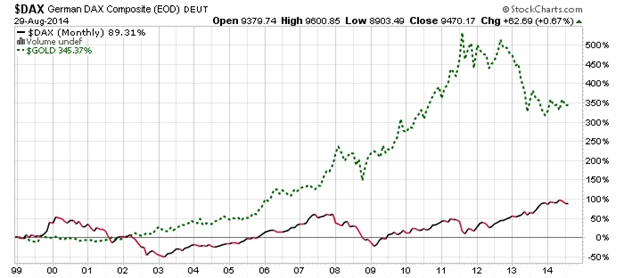

Global Intelligence









The Russian government and several of the country’s largest exporters have widely discussed the possibility of accepting payments in rubles for oil exports. Last week, Russia began to ship oil from the Novoportovskoye field to Europe by sea. Two oil tankers are expected to arrive in Europe in September.According to Kommersant, the payment for these shipments will be received in rubles.Gazprom Neft will not only accept payments in rubles; subsequent transfers via the ESPO may be paid for in yuan, the newspaper reported.According to the newspaper, the change in currency was made because of the Western sanctions against Russia.As a protective measure, Russia decided to avoid making its payments in US dollars, which can be tracked and controlled by the United States government, Kommersant reported.
The New New Normal flow of funds:
- Gazprom delivering gas to China.
- China Gazprom paying in Yuan (convertible into Rubles)
- Gazprom funding itself increasingly in Yuan.
- Russia buying Chinese goods and services in Yuan (convertible into Rubles)
And all of this with the US banker cartel completely disintermediated courtesy of the glaring absence of the USD in any of the above listed steps, or as some may call it: from the Petrodollar to the Gas-o-yuan (something 40 central banks have already figured out… just not the Fed).
In retrospect it will be very fitting that the crowning legacy of Obama’s disastrous reign, both domestically and certainly internationally, will be to force the world’s key ascendent superpowers (we certainly don’t envision broke, insolvent Europe among them) to drop the Petrodollar and end the reserve status of the US currency.

… A broad-based tax cut, for example, accommodated by a program of open-market purchases to alleviate any tendency for interest rates to increase, would almost certainly be an effective stimulant to consumption and hence to prices. Even if households decided not to increase consumption but instead re-balanced their portfolios by using their extra cash to acquire real and financial assets, the resulting increase in asset values would lower the cost of capital and improve the balance sheet positions of potential borrowers. A money-financed tax cut is essentially equivalent to Milton Friedman’s famous “helicopter drop” of money
 A year ago, when it became abundantly clear that all of the Fed’s attempts to boost the economy have failed, leading instead to a record divergence between the “1%” who were benefiting from the Fed’s aritficial inflation of financial assets, and everyone else (a topic that would become one of the most discussed issues of 2014) and with no help coming from a hopelessly broken Congress (who can forget the infamous plea by a desperate Wall Street lobby-funding recipient “Get to work Mr. Chariman”), we wrote that “Bernanke’s Helicopter Is Warming Up.”
A year ago, when it became abundantly clear that all of the Fed’s attempts to boost the economy have failed, leading instead to a record divergence between the “1%” who were benefiting from the Fed’s aritficial inflation of financial assets, and everyone else (a topic that would become one of the most discussed issues of 2014) and with no help coming from a hopelessly broken Congress (who can forget the infamous plea by a desperate Wall Street lobby-funding recipient “Get to work Mr. Chariman”), we wrote that “Bernanke’s Helicopter Is Warming Up.”To some extent, low inflation reflects intense competition in an increasingly globalized economy. But it also occurs when people and businesses are too hesitant to spend their money, which keeps unemployment high and wage growth low. In the eurozone, inflation has recently dropped perilously close to zero. And some countries, such as Portugal and Spain, may already be experiencing deflation. At best, the current policies are not working; at worst, they will lead to further instability and prolonged stagnation.Governments must do better. Rather than trying to spur private-sector spending through asset purchases or interest-rate changes,central banks, such as the Fed, should hand consumers cash directly. In practice, this policy could take the form of giving central banks the ability to hand their countries’ tax-paying households a certain amount of money. The government could distribute cash equally to all households or, even better, aim for the bottom 80 percent of households in terms of income. Targeting those who earn the least would have two primary benefits. For one thing, lower-income households are more prone to consume, so they would provide a greater boost to spending. For another, the policy would offset rising income inequality.
WASHINGTON (AP) — Taxes? Who wants to think about taxes around Labor Day?But if you count on your tax refund and you’re one of the millions getting tax credits to help pay health insurance premiums under President Barack Obama’s law, it’s not too earl…
Continue ReadingThe U.S. State Department spent more than $5 billion [11] dollars in pushing Ukraine towards the West. The U.S. ambassador to Ukraine (Geoffrey Pyatt) and assistant Secretary of State (Victoria Nuland) were also recorded plotting the downfall of the former Ukraine government in a leaked recorder conversation [12]. Top-level U.S. officials [13] literally handed out cookies [14] to the protesters [15] who overthrew the Ukrainian government.
And the U.S. has been doing everything it can to trumpet pro-Ukrainian and anti-Russian propaganda. So – without doubt – the U.S. government is heavily involved with fighting a propaganda war regarding Ukraine.
The United States and its European allies share most of the responsibility for the crisis. The taproot of the trouble is NATO enlargement, the central element of a larger strategy to move Ukraine out of Russia’s orbit and integrate it into the West. At the same time, the EU’s expansion eastward and the West’s backing of the pro-democracy movement in Ukraine — beginning with the Orange Revolution in 2004 — were critical elements, too. Since the mid-1990s, Russian leaders have adamantly opposed NATO enlargement, and in recent years, they have made it clear that they would not stand by while their strategically important neighbor turned into a Western bastion. For Putin, the illegal overthrow of Ukraine’s democratically elected and pro-Russian president — which he rightly labeled a “coup” — was the final straw. He responded by taking Crimea, a peninsula he feared would host a NATO naval base, and working to destabilize Ukraine until it abandoned its efforts to join the West. Putin’s pushback should have come as no surprise. After all, the West had been moving into Russia’s backyard and threatening its core strategic interests, a point Putin made emphatically and repeatedly. Elites in the United States and Europe have been blindsided by events only because they subscribe to a flawed view of international politics.
***
U.S. and European leaders blundered in attempting to turn Ukraine into a Western stronghold on Russia’s border. Now that the consequences have been laid bare, it would be an even greater mistake to continue this misbegotten policy.
***
The West’s final tool for peeling Kiev away from Moscow has been its efforts to spread Western values and promote democracy in Ukraine and other post-Soviet states, a plan that often entails funding pro-Western individuals and organizations. Victoria Nuland, the U.S. assistant secretary of state for European and Eurasian affairs, estimated in December 2013 that the United States had invested more than $5 billion since 1991 to help Ukraine achieve “the future it deserves.” As part of that effort, the U.S. government has bankrolled the National Endowment for Democracy. The nonprofit foundation has funded more than 60 projects aimed at promoting civil society in Ukraine, and the NED’s president, Carl Gershman, has called that country “the biggest prize.” After Yanukovych won Ukraine’s presidential election in February 2010, the NED decided he was undermining its goals, and so it stepped up its efforts to support the opposition and strengthen the country’s democratic institutions.
When Russian leaders look at Western social engineering in Ukraine, they worry that their country might be next. And such fears are hardly groundless. In September 2013, Gershman wrote in The Washington Post, “Ukraine’s choice to join Europe will accelerate the demise of the ideology of Russian imperialism that Putin represents.” He added: “Russians, too, face a choice, and Putin may find himself on the losing end not just in the near abroad but within Russia itself.”
The West’s triple package of policies — NATO enlargement, EU expansion, and democracy promotion — added fuel to a fire waiting to ignite. The spark came in November 2013, when Yanukovych rejected a major economic deal he had been negotiating with the EU and decided to accept a $15 billion Russian counteroffer instead. That decision gave rise to antigovernment demonstrations that escalated over the following three months and that by mid-February had led to the deaths of some one hundred protesters. Western emissaries hurriedly flew to Kiev to resolve the crisis. On February 21, the government and the opposition struck a deal that allowed Yanukovych to stay in power until new elections were held. But it immediately fell apart, and Yanukovych fled to Russia the next day. The new government in Kiev was pro-Western and anti-Russian to the core, and it contained four high-ranking members who could legitimately be labeled neofascists.
Although the full extent of U.S. involvement has not yet come to light, it is clear that Washington backed the coup. Nuland and Republican Senator John McCain participated in antigovernment demonstrations, and Geoffrey Pyatt, the U.S. ambassador to Ukraine, proclaimed after Yanukovych’s toppling that it was “a day for the history books.” As a leaked telephone recording revealed, Nuland had advocated regime change and wanted the Ukrainian politician Arseniy Yatsenyuk to become prime minister in the new government, which he did. No wonder Russians of all persuasions think the West played a role in Yanukovych’s ouster.
***
Putin’s actions should be easy to comprehend. A huge expanse of flat land that Napoleonic France, imperial Germany, and Nazi Germany all crossed to strike at Russia itself, Ukraine serves as a buffer state of enormous strategic importance to Russia. No Russian leader would tolerate a military alliance that was Moscow’s mortal enemy until recently moving into Ukraine. Nor would any Russian leader stand idly by while the West helped install a government there that was determined to integrate Ukraine into the West.
Washington may not like Moscow’s position, but it should understand the logic behind it. This is Geopolitics 101: great powers are always sensitive to potential threats near their home territory. After all, the United States does not tolerate distant great powers deploying military forces anywhere in the Western Hemisphere, much less on its borders. Imagine the outrage in Washington if China built an impressive military alliance and tried to include Canada and Mexico in it. Logic aside, Russian leaders have told their Western counterparts on many occasions that they consider NATO expansion into Georgia and Ukraine unacceptable, along with any effort to turn those countries against Russia — a message that the 2008 Russian-Georgian war also made crystal clear.
***
In [a] 1998 interview, [the top American expert on Russia, George] Kennan predicted that NATO expansion would provoke a crisis, after which the proponents of expansion would “say that we always told you that is how the Russians are.” As if on cue, most Western officials have portrayed Putin as the real culprit in the Ukraine predicament.
There is a solution to the crisis in Ukraine, however — although it would require the West to think about the country in a fundamentally new way. The United States and its allies should abandon their plan to westernize Ukraine and instead aim to make it a neutral buffer between NATO and Russia, akin to Austria’s position during the Cold War. Western leaders should acknowledge that Ukraine matters so much to Putin that they cannot support an anti-Russian regime there. This would not mean that a future Ukrainian government would have to be pro-Russian or anti-NATO. On the contrary, the goal should be a sovereign Ukraine that falls in neither the Russian nor the Western camp.
***
The United States and its European allies now face a choice on Ukraine. They can continue their current policy, which will exacerbate hostilities with Russia and devastate Ukraine in the process — a scenario in which everyone would come out a loser. Or they can switch gears and work to create a prosperous but neutral Ukraine, one that does not threaten Russia and allows the West to repair its relations with Moscow. With that approach, all sides would win.
On one hand, despite initial weakness following Europe’s triple-dip red alert, futures declined only to surge higher after some headline or another out of Russia was again spun to suggest imminent Ukraine de-escalation (something which Russia whose onl…
Continue ReadingNot only is the US sanctioning Russian banks and companies, but it also is trying to strong-arm European banks into enacting harsh sanctions against Russia as well. Given the amount of business that European banks do with Russia, European sanctions could hurt Europe at least as much as Russia. At the same time the US expects cooperation from European banks, it is also prosecuting those same banks and fining them billions of dollars for violating existing US sanctions. It is not difficult to imagine that European banks will increasingly become fed up with having to act as the US government’s unpaid policemen, while having to pay billions of dollars in fines every time they engage in business that Washington doesn’t like.
European banks are already cutting ties with American citizens and businesses due to the stringent compliance required by recently-passed laws such as FATCA (Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act). In the IRS’s quest to suck in as much tax dollars as possible from around the world, the agency has made Americans into the pariahs of the international financial system. As the burdens the US government places on European banks grow heavier, it should be expected that more and more European banks will reduce their exposure to the United States and to the dollar, eventually leaving the US isolated. Attempting to isolate Russia, the US actually isolates itself.
Another effect of sanctions is that Russia will grow closer to its BRICS (Brazil/Russia/India/China/South Africa) allies. These countries count over 40 percent of the world’s population, have a combined economic output almost equal to the US and EU, and have significant natural resources at their disposal. Russia is one of the world’s largest oil producers and supplies Europe with a large percent of its natural gas. Brazil has the second-largest industrial sector in the Americas and is the world’s largest exporter of ethanol. China is rich in mineral resources and is the world’s largest food producer. Already Russia and China are signing agreements to conduct their bilateral trade with their own national currencies rather than with the dollar, a trend which, if it spreads, will continue to erode the dollar’s position in international trade. Perhaps more importantly, China, Russia, and South Africa together produce nearly 40 percent of the world’s gold, which could play a role if the BRICS countries decide to establish a gold-backed currency to challenge the dollar.
US policymakers fail to realize that the United States is not the global hegemon it was after World War II. They fail to understand that their overbearing actions toward other countries, even those considered friends, have severely eroded any good will that might previously have existed. And they fail to appreciate that more than 70 years of devaluing the dollar has put the rest of the world on edge. There is a reason the euro was created, a reason that China is moving to internationalize its currency, and a reason that other countries around the world seek to negotiate monetary and trade compacts. The rest of the world is tired of subsidizing the United States government’s enormous debts, and tired of producing and exporting trillions of dollars of goods to the US, only to receive increasingly worthless dollars in return.
The US government has always relied on the cooperation of other countries to maintain the dollar’s preeminent position. But international patience is wearing thin, especially as the carrot-and-stick approach of recent decades has become all stick and no carrot. If President Obama and his successors continue with their heavy-handed approach of levying sanctions against every country that does something US policymakers don’t like, it will only lead to more countries shunning the dollar and accelerating the dollar’s slide into irrelevance.
Follow GIH and get free updates on Global Intelligence, Analysis, and more.