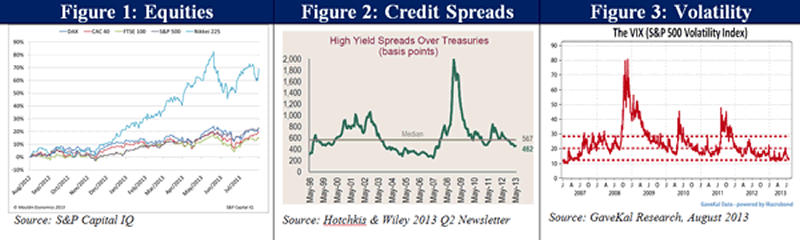
What in the world is going on?! As I write this letter from the Maine woods, the S&P 500 has just cleared 1,700 for the first time. The German DAX continues to set all-time highs above 8,400. The United Kingdom’s FTSE 100 is quickly approaching its 1999 record high of 6,930, and its mid-cap cousin, the FTSE 250, just broke through to its all-time level above 15,000. And last but not least, Japan’s Nikkei 225 is extending its gains once more, toward 14,500. This weekend I am sitting around with some of the smartest economic and trading minds in the country. At Leen’s Lodge, where we’re fishing and eating where our phones don’t work, the question on our minds is, how long can this run go on? The debates can get intense in a room full of strong opinions.
So, with a little help, I did some research on what our forward-looking prospects are for the markets. Let me take this opportunity to introduce a new name to readers, one that will become familiar over the next few years. I have gotten to know Worth Wray, a young economist (though I should say that, as I stare 64 in the face, a lot of people are looking young these days) who has really impressed me with the breadth of his knowledge and insights. He was the former portfolio strategist for my good friends at Salient down in Houston, and they were kind enough to let me entice him to come to Dallas to work with me. This is a big move for both of us, and I am finding that it’s one I should have undertaken a long time ago. Worth is really going to help me expand my abilities to do research and present my thoughts to you. I asked him a few questions, and he helped me tee up this week’s letter. Plus, we’ll look across the Pacific, and I’ll share some though ts I’ve had about an interesting black swan that could be developing in the Korean Peninsula. Let’s get started!
To many investors, developed markets appear healthier and stronger than they have in years. Major equity markets are rallying to record highs; corporate credit spreads are tight versus US Treasuries and getting tighter; and broad measures of volatility continue to fall to their lowest levels since 2007.
This kind of news would normally point to prosperity across the real economy and call for a celebration – but prices do not always reflect reality. Moreover, the combination of high and rising valuations, low volatility, and a weakening trend in real earnings growth is a proven recipe for poor long-term returns and market instability.
Let’s take the S&P 500 as an example. It returned roughly 42% from September 1, 2011, through August 1, 2013, as the VIX Index fell to its lowest levels since the global financial crisis. Over that time frame, real earnings declined slightly (down about 2% through Q1 2013 earnings season), while the trailing 12-month price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio jumped 44%, from 13.5x to 19.5x. That means the majority of the recent gains in US equity markets were driven by multiple expansion in spite of negative real earnings growth. This is a clear sign that sentiment, rather than fundamentals, is driving the markets higher.
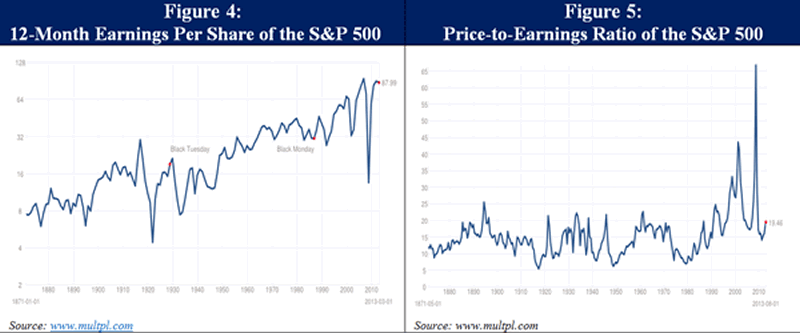
Of course, the simple trailing 12-month P/E ratio can be misleading at critical turning points if you are trying to handicap the potential for long-term returns. For example, the collapse in real earnings during the global financial crisis sent the S&P 500’s trailing P/E multiple through the roof by March 2009. So, while trailing P/E is a useful tool for understanding what has already happened in the market, the “Shiller P/E” is far more useful for calculating a reasonable range of expected returns going forward. This approach won’t help you much with short-term market timing, but current valuations have historically proven extremely useful in forecasting long-term returns. In his book Irrational Exuberance (2005), Robert Shiller of Yale University shows how this approach “confirms that long-term investors – investors who commit their money to an investment for ten full years – did do well when prices were low rel ative to earnings at the beginning of the ten years. Long-term investors would be well-advised, individually, to lower their exposure to the stock market when it is high … and to get into the market when it is low.”
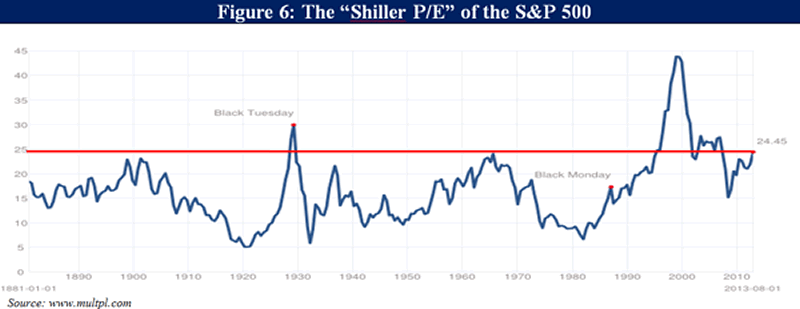
As you can see in Figure 6, compared to the more common trailing 12-month P/E ratio in Figure 5, the Shiller P/E metric essentially smooths out the series and helps us avoid false signals by dividing the market’s current price by the average inflation-adjusted earnings of the past ten years. Historically, this range has peaked and given way to major market declines at around 29x on average (or 26x excluding the dot-com bubble), and it has bottomed in the mid-single digits. Not only does today’s Shiller P/E of 24x suggest a seriously overvalued market, but the rapid multiple expansion of the last two years in the absence of earnings growth suggests that this market is also seriously overbought.
John Hussman helps us keep current valuations in historical perspective:
The Shiller P/E is now 24.4, about the same level as August 1929, higher than December 1972, higher than August 1987, but less extreme than the level of 43 that was reached in March 2000 (a level that has been followed by more than 13 years of market returns within a fraction of a percent of the return on Treasury bills – and even then only by revisiting significantly overvalued levels today). The Shiller P/E is presently moderately below the level of 27 at the October 2007 market peak. It’s worth noting that the 2000-2001 recession is already out of the Shiller calculation. Moreover, looking closely at the data, the implied profit margin embedded in today’s Shiller P/E is 6.3%, compared with a historical average of only about 5.3%. At normal profit margins, the current Shiller P/E would be 29.
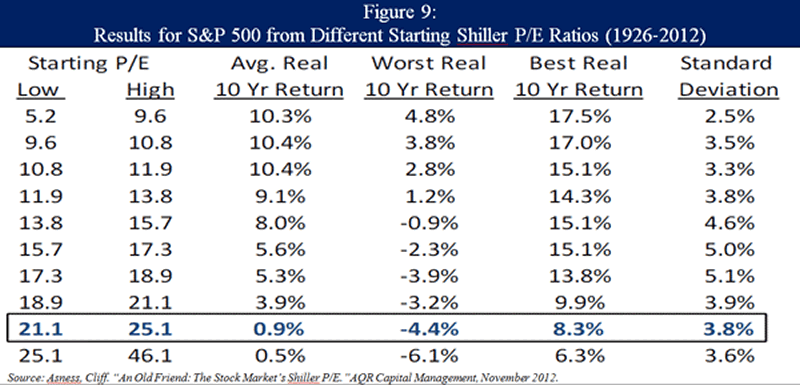
While it may be impossible to accurately predict when this policy-driven market will break, history suggests it would be very reasonable for the secular bear to eventually bottom at a P/E multiple between 5x and 10x, opening up one of the rare wealth-creation opportunities to deploy capital at truly cheap prices. Some of these technical details are rather dry, but I hope you’ll focus on the main idea: We are not talking about the potential for a modest 20% to 30% drawdown in the S&P 500. If history is any indication, we are talking about the potential for a 50%+ peak-to-trough drawdown and ten-year average annual returns as bad as -4.4%, according to the chart above from Cliff Asness at AQR. Such a result would fall in line with somewhat similar deleveraging periods such as the United States experienced in the 1930s and Japan has experienced since 1989. There is no way to sugarcoat it: too much equity risk can be unproductive and even destructive in this kind of economic environment.
But where there is danger, there is also opportunity. This is a terrific time to take some profits and diversify away from the growth-oriented risk factors that dominate most investors’ portfolios. Instead of concentrating risk in one asset class or one country, investors can boost returns and achieve more balance by taking a global view, by broadening the mix of core asset classes, and by weighting those return streams to achieve balance across potential economic outcomes (rather than trying to predict the future). Since equities and credit are essentially a directional bet on positive economic growth and benign inflation, you have a lot to gain from diversifying into other core market risks: commodities, which thrive when inflation, or more specifically expected inflation, is rising; and nominal safe-haven government bonds, which thrive as inflation gives way to deflation and the oth er assets typically decline. While each group of asset classes responds to economic conditions differently and exhibits low correlations to the others, each of them tends to offer similar risk-adjusted returns over long periods of time, thus warranting constant inclusion in any core portfolio.
It also makes sense to embrace truly diversifying alternative strategies that are either less correlated or negatively correlated. When valuations are expensive across the board, momentum-based strategies like managed futures can be a fantastic addition to a portfolio. Aside from government bonds, momentum is the only easily accessible strategy that tends to become more negatively correlated with broader markets during times of extreme stress and tends to deliver outsized returns when your other investments are losing money.
Of course, combining the asset classes into one portfolio is the hard part, but research going back to the early 1970s suggests that broadening this mix of core assets – so that you have some element of your portfolio that responds positively to every potential economic season – and managing the relative allocations to each economic scenario may be your biggest opportunity to add value in the investing process.
You have a lot to gain from diversifying as broadly as possible, eliminating unrewarded costs, reducing your reliance on equity risk, and reining in the emotional mistakes that often lead investors to dramatically underperform. Remember, in a world characterized by deleveraging, changing demographics in aging populations, financial repression, and increasingly experimental monetary policy, every basis point counts and anything can happen.
With that, let’s end our discussion with a few words of advice from the world’s largest and arguably most successful hedge fund manager, Ray Dalio:
What I’m trying to say is that for the average investor, what I would encourage them to do is to understand that there’s inflation and growth. It can go higher and lower and to have four different portfolios essentially that make up your entire portfolio that gets you balanced. Because in every generation, there is some period of time, there’s a ruinous asset class, that will destroy wealth and you don’t know which one that will be in your life time. So the best thing you can do is have a portfolio that is immune, that is well diversified. That is what we call an all-weather portfolio. That means you don’t have a concentration in that asset class that’s going to annihilate you and you don’t know which one it is.
Last week I was in Newport, Rhode Island, at the Naval War College, where I participated in a summer study group focused on possible futures and how they might affect the strategy of the US Defense Department. The discussions were wide-ranging and mind-expanding, at least for me. As readers know, I believe that Japan has begun a long-term process of continually devaluing its currency. For reasons I have written about at length in previous letters, I think the yen could go to 200 to the dollar in the next five years. I don’t see a precipitous move, simply a steady erosion as Japan tries to bring back inflation and export its deflation.
While the yen at its current valuation is not a particular problem for the rest of the world, when it hits 120 we will start to see raised eyebrows and political speeches from the countries most affected. At 140 we could start to see serious reactions.
One of the countries that I think is put into a most difficult situation is South Korea. Their options for responding to a weakening yen are quite limited. If they respond by printing more of their own currency, they are likely to engender a debilitating inflation, which is of course not a good thing. Protectionism will have little real effect vis-à-vis Japan. Remember that the Japanese yen was 357 to the dollar about 40 years ago. The Japanese watched their currency rise by almost 400% in the decades since. The only real response available to them was to simply become more competitive and more productive as their currency got stronger, and to their great credit they did.
Honing their competitive edge may also be the only real option for South Korea. But it is not an easy one, of course, and you will hear lots of complaints from Korean politicians and businessmen. Not an easy environment, to be sure.
Now let’s shift our focus to North Korea. Everyone (including your humble analyst) is worried about the isolationist regime in North Korea having access to nuclear weapons and the ability to deliver them on missiles. But a few conversations I had this past week led me to think there is another scenario we should consider.
A side conversation at the study group began with an observation by a senior officer about the ability of the North Korean military to actually project power. As this information is nothing more than what you can find in the newspapers, I feel comfortable discussing it here. Everyone knows that North Koreans have been malnourished for multiple decades. Studies suggest that North Koreans may be up to three inches shorter than South Koreans and have diminished IQs because of malnourishment as children. The latter is a known effect on human beings anywhere who are subjected to a starvation diet. The North Korean population has suffered from severe diet restriction for decades.
How capable is the North Korean military of actually mounting an offensive when their soldiers are simply not physically able to withstand the pressures of combat? I was also able last week to visit with one of the great geopolitical strategists of our time, Professor Ian Bremmer of Columbia, who is the president and founder of Eurasia Group, with some 100 geopolitical analysts working for him. I shared with him my concerns about the Korean peninsula. He immediately said that he was more worried about the Korean peninsula than any other part of the world, including the Middle East. One of the interesting things that he shared is that an increasing number of cell phones are being smuggled into North Korea from China and that the North Koreans are beginning to get the real story about the world rather than just the propaganda fed to them by their government.
While there is little ability for the North Korean population to actually stage a revolution, as they do not have the weapons and hungry people really have difficulty mounting military operations, there is the possibility of the country becoming increasingly difficult to manage. Combine that with the potential for a disastrous food-production year, and the potential for the collapse of the government is not all that far-fetched.
There were not many people forecasting the collapse of the USSR in 1987. Yet as we look back, the confluence of causes that resulted in its collapse seems rather obvious. Probably, the current dictatorship will maintain its stranglehold on North Korea. That is the tendency with repression and tyranny – witness Cuba and any number of other countries. But one cannot dismiss the possibility of a collapse of the North Korean state.
If that were to happen it would be a humanitarian disaster. In the long run it might be better for the North Korean people, but in the short run it would be catastrophic. It is not unreasonable to expect that South Korea would have to do the bulk of the heavy lifting, especially after the first year or so. And should the world no longer have to focus on the ability of North Korea to create mischief with nuclear weapons, North Korea could soon become page 16 news.
No matter how positively you would want to view Korean unification, the process would be enormously expensive for South Korea. Assimilating a population long challenged by hardship into a new reality, not to mention incorporating it into a modern economic model, is a daunting challenge. I think the task would be more difficult and more expensive on a per-capita basis than the unification of Germany.
And this could happen while the attention of South Korea is focused on dealing with the devaluation of the yen and the need to become progressively more competitive to maintain its export and business model. There is also the possibility of massive refugee movements into China. That is a significantly different issue than worrying about a million-man army crossing the DMZ into South Korea.
I’m not saying this will happen, but it is a possibility we need to keep an eye on.
Like this:
Like Loading...